|
Network of Excellence |
CARiMan |
The Internet Portal for Computer Aided Risk Management |
TI:
Transmission and interfaces, security of data transmission
Responsible: UniCr
Assistance: UNIMI,
UoO, all
partners
Objectives
JPA TI deals with transmission and interfaces and the
security of data transmission. The
objectives of this JPA are:
-
To demonstrate why risk management monitored systems are so vulnerable to destruction, error, abuse, and system quality problems. More specifically, to perform and validate a throughout analysis of possible threats to monitoring systems, including specific requirements as low computing power, low power consumption and the close proximity of the ubiquitous cell phone radiating up to 2 W of GHz power.
-
To ensure that the CARiMan project confirms with and contributes to European standards (CEN/TC 251) and International standards for security regulations.
-
To compare general controls and application controls for electronic risk management information systems through a consistent analysis of existing systems, as to derive their weakness and learn from previous failures.
-
To evaluate the special measures required ensuring the reliability, availability, confidentiality and security of electronic risk management records and digital transmission process.
-
To describe the most important software quality assurance techniques and propose a set of measures to warrant the transported data as much authenticity, integrity and confidentiality as technically possible.
-
To demonstrate the importance of the auditing information systems and safeguarding data quality.
-
To define management solutions for TI: Transmission and interfaces, security of data transmission.
-
To define technology solutions and organizational requirements of security issues
A key deliverable for the entire CARiMan project is the
provision of security mechanisms to cover all aspects of the effective use and
management of the European technical standards for data capture and
transmission. Specifically developed toolsets will be made available to manage,
update and access this central technology to support confidential information.
Problems of security and data protection are important in applications
associated with embedded and portable systems. Examples include security for
wireless phones, wireless computing or other applications that demand
coding/decoding or advanced methods of authentication. Data transmission in a
monitoring system shall be resistant to the following threats:
·
malicious action: unlawful retrieval of data from a
monitored system record for any purpose
·
non-malicious action: data loss or data corruption due
to normal impairments in the transmission system, long transmission delay, data
flow interrupted for a time ranging from minutes to days caused by network
overload, traffic saturation, and broken communication equipment, etc.
The first kind of problems relates with issues of data
security, whereas the second one is associated with the design of the
communication platform. Both of these types of problems are dealt with along the
lines of this JPA.
Cryptography allows us to address problems of malicious
acts in data communication. The implementation of cryptographic systems presents
several requirements and challenges. First, the performance of the algorithms is
often crucial. One needs encryption algorithms to run at the transmission rates
of the communication links. In addition to performance requirements,
guaranteeing security is a formidable challenge. An encryption algorithm running
on a general-purpose computer has only limited physical security, as the secure
storage of keys in memory is difficult on most operation systems. On the other
hand, hardware encryption devices can be securely encapsulated to prevent
attackers from tampering with the system. Thus, a general-purpose computer is
the platform of known drawback of reduced flexibility and potentially high
costs. These drawbacks are especially prominent in secure applications, which
are designed using new secure protocol paradigms.
Field Programmable Gate Array, or FPGA devices combine the flexibility of
software on general-purpose computers with the hardware speed and better
physical security than general-purpose computers.
Owing to the above considerations, it is desirable to
implement cryptographic algorithms in hardware to achieve optimal system
performance while maintaining physical security. That kind of implementation is
able to enhance the means of automatic hardware synthesis of cryptographic
algorithms and as consequence to enhance substantially the productivity of the
process of cryptographic algorithm hardware synthesis and to enhance the quality
and reduce the time and the cost of cryptographic devices synthesized. Thus,
along the duration of the project we will conduct the necessary research and
analysis activities taking into account the advisories of security approaches
with respect to the legal aspects of health telematics, in order to implement a
secure and reliable information system, which has the following architecture.
Cryptographic algorithms can not be considered as absolutely safe. It is well
known that embedding a cryptographic algorithm or a key, even through hardware
(e.g. a FPGA), does not result in secure encryption. A chip can be analyzed,
either electrically or by stripping it layer by layer, in order to derive its
schematic. Therefore, key distribution is normally a major issue and many system
of the past failed at this issue. In our project special attention will be
devoted to this point and a careful selection of available cryptographic
systems, with both public and secret keys, will be performed. We should
emphasize, however, that a trade off always exist between cost and expected
protection level.
Within the CARiMan project, we need to view TI in
association with other project components as in the Figure bellow. Thus, within
TI we need to cover two types of communications:
·
With the outside world:
between C7 and PD that can be wireless or regular connection with devices
·
Intra-system:
between PD and SP, SP and KM, KM and C4 that must enable all the security
issues.
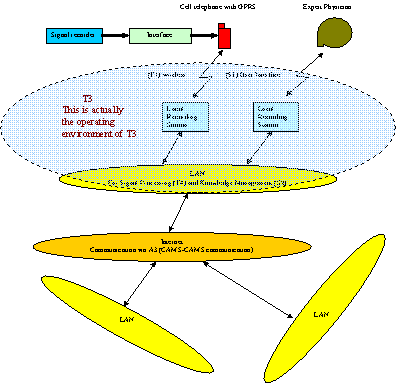
Fig.TI.1:
Intrasystem
CARiManS communications module (TI) in association with intersystem
communications
By looking at Fig. TI.1 we can deduct the paramount importance of security in all aspects of information flow. A communications platform will be built in order to accommodate Advanced Risk Management Services Provision that will incorporate all the latest security protocols in order to ensure protection off all sensitive data, security, authenticity and confidentiality.